When it comes to ecommerce development, there are several different models that businesses can follow, depending on their specific needs. Understanding these models is crucial for anyone looking to succeed in the online marketplace. E-commerce is more than just selling products; it’s about choosing the right approach for your business, whether you’re a small retailer or a large enterprise. This guide will help you understand the various types of e-commerce models and how they function.
E-Commerce Design and Development
ecommerce design and development play a pivotal role in creating a seamless experience for users. Whether it’s navigating through product categories, browsing through listings, or making a purchase, the design must be intuitive and responsive. In B2C models, design elements that encourage impulsive buying, such as clear product images, easy navigation, and a smooth checkout process, are critical. For B2B commerce businesses, the platform may require more advanced features like product catalogs, personalized pricing, or account management for large buyers.
The design should not only be aesthetically pleasing but also highly functional. User-friendly interfaces, fast load times, and mobile responsiveness are essential aspects of e-commerce design that directly impact sales and customer satisfaction.
“Here we have included some services for you which you can read from here“
- Differences Web Development and Mobile App Development
- Machine Learning APIs
- Convert HTML Website To PHP
- Top Mobile Application Development Service
- Top IT Consulting Services
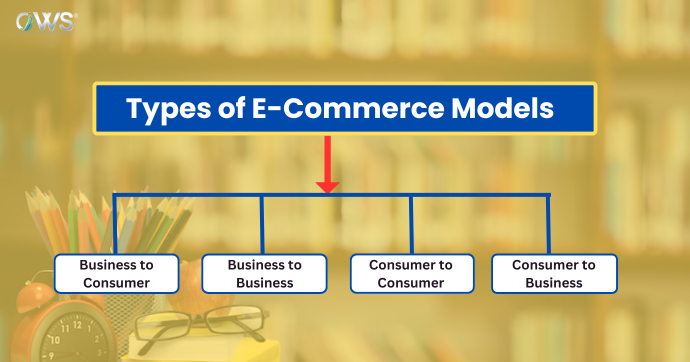
Types of E-Commerce Models
When we talk about e-commerce, there are four main types of e-commerce models, each designed to serve different kinds of markets and business needs. Understanding these models can help businesses choose the right path for their online ventures.
1. Business to Consumer (B2C)
In the B2C model, the process is quite simple and user-friendly. A consumer visits an online store, browses through the available products, adds items to the shopping cart, and makes a purchase. This entire process is usually quick, with minimal interaction between the business and the consumer beyond the transaction. The primary goal in B2C is to ensure an easy and satisfying shopping experience for the customer, focusing on convenience and speed. Payment is typically made through integrated payment gateways, and delivery options are presented at checkout.
2. Business to Business (B2B)
On the other hand, B2B e-commerce operates with more complexity. Transactions in this model involve two businesses, and the purchasing process may require negotiations, bulk orders, and long-term contracts. B2B transactions often take longer to finalize as companies need to align on pricing, terms, and delivery schedules. These transactions are crucial for businesses that rely on a steady supply of goods and services. The relationship between the two businesses in B2B models tends to be long-term, and many orders are recurring. Since B2B deals with larger volumes and higher value, both businesses often go through multiple rounds of communication before an order is completed.
3. Consumer to Consumer (C2C)
In C2C, the process is more peer-to-peer. One consumer lists an item for sale, while another consumer browses and buys that item. Platforms like eBay or Craigslist facilitate these transactions, but the individuals involved handle most of the communication and payment processes. While the platform may provide some security features, the exchange is primarily between two private individuals. In this model, the success of a transaction largely depends on the platform’s ability to connect buyers and sellers and provide a smooth experience.
4. Consumer to Business (C2B)
The C2B model works in a reverse fashion where consumers offer goods, services, or skills to businesses. The consumer might list their products or services on a marketplace where businesses come to purchase from them. For instance, a freelancer offering digital services such as graphic design or photography might bid for projects or sell their work directly to businesses. In this model, the business selects a consumer (provider) based on the quality and suitability of the offer.
How E-Commerce Models Work
Each e-commerce model operates in a slightly different way. In B2C, the process is relatively straightforward: a consumer visits a website, selects a product, and makes a purchase. On the other hand, B2B transactions often involve negotiation and contracts before a deal is finalized.
Custom Solutions with E-Commerce Development Services
For businesses that want to stand out from the competition, ecommerce development services offer tailored solutions that meet specific needs. Whether it’s adding new features or optimizing an existing platform, development services can ensure that the website functions perfectly across all devices. These services include creating custom integrations, like connecting the platform to payment gateways, inventory systems, or customer relationship management tools.
Conclusion
For many businesses, selecting the right platform is a crucial step in their e-commerce journey. Platforms like Magento offer specialized solutions through Adobe Commerce development services, designed to handle the complexities of large-scale e-commerce operations.
Tags-: